Core Web Vitals should be addressed by any web design company.
Your website contains essential indications that indicate Google it’s in top shape, much like the human body has vital signals to demonstrate it’s in excellent functioning order.
Google is presently implementing algorithm adjustments that will have an effect on your rankings, therefore they’re important. In fact, we’d go so far as to suggest that Core Web Vitals are the most critical aspect of your website to consider in mid-2021 and beyond.
We’ll look at the whats and whys of basic web vitals in this blog article, then give you some pointers on how to bring your site up to speed.
What are Google’s Web Essentials?
Google has provided Web Vitals as standards to eliminate any subjectivity surrounding what makes a website excellent. These are divided into two categories: Core Web Vitals and Other Web Vitals. The Core Web Vital metrics are field-measurable and indicate a user-centric outcome, therefore Google urges designers and developers to concentrate on them.
Core Web Vitals consist of: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). In order to evaluate your organic SEO rankings, Google collects these variables in addition to the current pool of SEO signals.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
LCP is a loading performance measure. It determines how long it takes for your site’s most important content piece (above-the-fold) to become completely displayed. To offer a pleasant user experience, Google recommends that LCP occur within 2.5 seconds.
First Input Deplay (FID)
FID is a statistic that measures how interactive a user is. It determines how long it takes for the user to be able to click, scroll, or interact with the website after it has fully loaded. To offer a pleasant user experience, Google recommends that FID occur within 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
CLS is a visual stability metric. It counts the number of site components that changed position from the beginning to the end of the load, and it grows as more things are moved and by how much. CLS should be kept below 0.1 in order to give a decent user experience, according to Google.
Because CLS isn’t as clear as time, here are some scenarios it detects:
- When you try to click a link, the location of the link shifts as the page loads, forcing you to click on the wrong object.
- When you’re reading an article, the website content moves, and you lose your spot.
- When you’re gazing at a picture, the website jumps, and you’re forced to stare at a banner or commercial.
These new indications come down to having a website that is quick to load and navigate. If these indicators are lower than the suggested ratings, you will not be removed from search engine results; nevertheless, ignoring them will allow your rivals to leapfrog you in the rankings.
Why are Google’s Core Web Vitals important?
You’ll want to get your website in front of as many people as possible because it’s a lead-generating income instrument. And it can only do so when consumers are searching for it on search engine result pages (SERPs). You’ll be in a better position to optimize and increase your position if you understand the elements that play into your page’s rating.
Another benefit of following Google’s Core Web Vitals is that it gives your consumers a consistent user experience, which leads to increased purchases. On the other hand, it limits what may be done above-the-fold without having a detrimental impact on your rankings. To have a successful online presence in 2021 and beyond, you’ll need to strike a balance between these opposing factors.
What are the Core Web Vitals of your website?
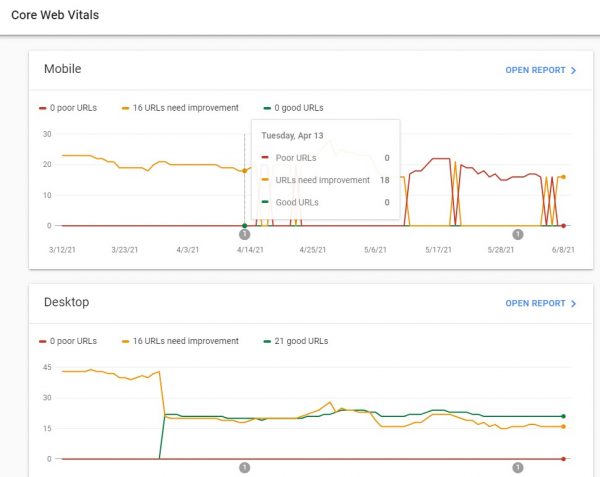
The good news is that Google’s Search Console automatically reports Core Web Vitals via their Chrome UX report (CrUX) report. The web essential data obtained when actual users visit your website is used to create this report. Each page of your website is scanned, and the information is converted into Core Web Vital metrics and graphed over time.
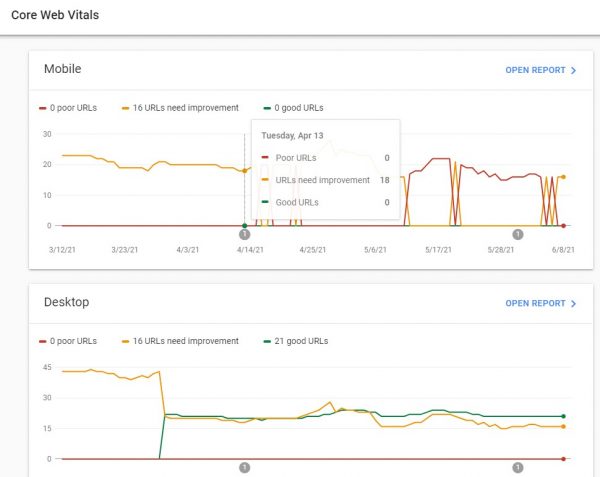
Because this is real user data, also known as Field Data, you may only get data on these reports if your website has a sufficient number of visitors. Any optimizations, however, may not be immediately visible in these reports. To help with this, you may use a number of testing tools to see if your optimizations are progressing in the correct direction.
What is the best way to test a website’s Core Web Vitals?
There are several tools available to let you test Core Web Vitals on your own. While these are tools to help you optimize your website, the data collected from testing tools, also known as Lab Data, is not utilized in the SERPs. Here are a few tools that we think you should try:
Paid options are available if you want your testing to be more accurate for your target demographic or device. You may use this tool to test from several countries, throttle the connection, and test from a variety of devices. It’s worth noting that GTMetrix employs a statistic known as Total Blocking Time (TBT), which is meant to resemble Google’s FID score.
This is based on Google’s Page Speed data centers, which may or may not reflect the locations of your target users. Google’s servers, according to internet sources, are located in Taiwan, Europe (Netherlands), and the United States (Oregon & South Carolina).
Lighthouse
This is Google’s own tester, which you may access using the Chrome browser. When you check a website, you may use it to conduct tests on your own computer.
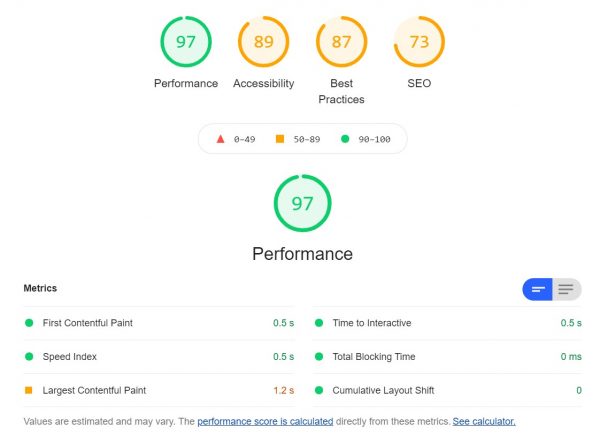
It’s worth noting that Google utilizes mobile-first crawling, which implies that smartphone scores are prioritized above desktop scores. Another issue is that while evaluating the mobile experience, Google’s algorithm throttles the internet speed and CPU they utilize. Websites that are developed with mobile speeds in mind have an advantage over their competitors.
How can you enhance the Core Web Vitals of your website?
Improve your hosting
While it may be tempting to choose the cheapest hosting plan, this may negatively impact your website’s performance and, as a result, your results in the long term. Choose a reputable host who is near to your target market.
Improve your website
If you don’t have the resources to hire a developer, search for a service or plugin that can help you with the following:
- Gzip Compression
- Image Compression
- Website Caching
- Deferring Scripts, Styling, Fonts
- Content Delivery Networks (CDN) – if your target market is multi-country
Remove unnecessary plugins
Optimize your images & videos
Images and videos can cause a website to load slowly, so don’t make them any larger than necessary. You may accomplish this using a number of different image/video optimizing programs.
To avoid affecting your CLS ratings, always give a height and width for your pictures (and videos).
Fine-tune your JavaScript
Heavy JavaScript usage is generally the cause of poor FID findings. Javascript is commonly used to enhance a website’s mouse operation or to add visual elements. While you won’t be able to change anything without the help of a web developer, make sure you keep your JavaScript usage to a minimum by eliminating any superfluous UI effects or functionality.
Share this:

Client’s review for our work satisfaction.

They were great! I had a great experience working with FSM. They redesigned my company website to become a mobile friendly site. They were very responsive, agile and always willing to help. They were also very fast and managed to deliver our website well before the expected deadline.
Michael Solano
CEO - Geotrek Land Surveyor
FSM is an expert IT Company. Franky helped me with my website. He is a careful and attentive listener. I admire his efforts and am pleased with his performance. He gets 5 stars from me. He is unrivaled. Thank you
Richard Rigosa
Realtor
Highly suggested for those looking to increase their online presence at a low cost. We received excellent service and commendable performance in a short period of time for a fraction of the cost. Excellent customer support!
Joan Nami
Entrepreneur
